If you see the message System detected an address conflict for IP address, this guide walks through seven practical fixes to resolve it. Address conflicts occur when two devices use the same IPv4 address on the same network, which can cause loss of connectivity, slow response times, or intermittent drops.

Page Contents
System detected an address conflict for IP address -7 Fixes
Try each fix one at a time and test your connection after each step. Use an administrator account when required.
Fix 1: Restart the router, modem, and affected devices
Power-cycle your router and modem, then restart the PC or device showing the error. This forces DHCP to reassign addresses and often clears transient conflicts. If possible, disconnect other devices briefly to determine which one reappears with the same IP address.
Fix 2: Release and renew the IP address
If your device has picked up an IP already used by another device, releasing and renewing your current address forces Windows to request a fresh one from the router. This is one of the quickest ways to clear duplicate IP conflicts.
1. Open Command Prompt as administrator.
2. Run: ipconfig /release
3. After that, run: ipconfig /renew
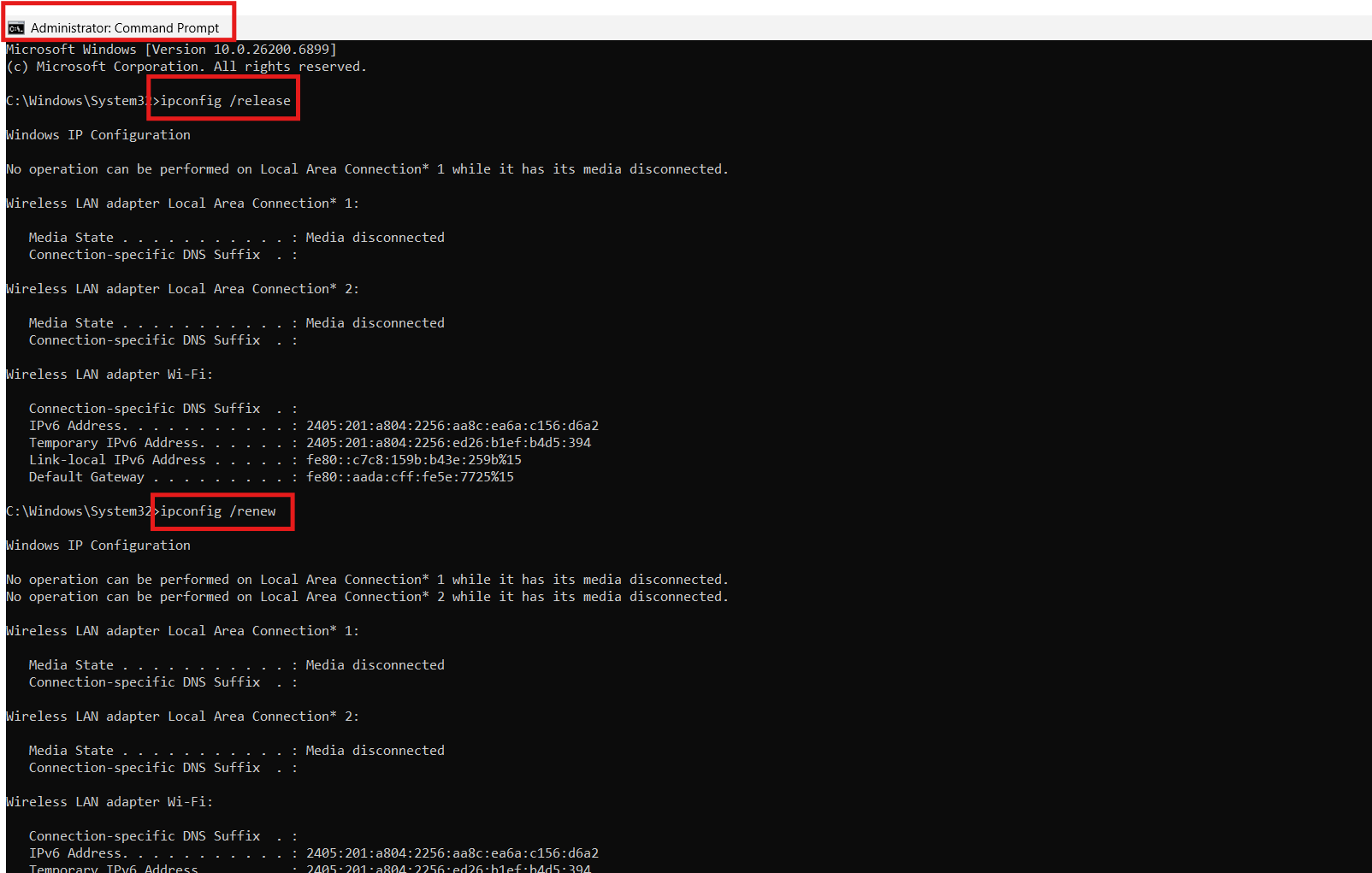
4. Wait for the new IP address to be assigned, then test your connection.
Fix 3: Reset TCP/IP stack and Winsock
Corrupted TCP/IP components can also cause repeated address conflicts. Resetting these networking modules helps restore default communication settings and removes faulty configurations.
1. Open Command Prompt (Admin).
2. Run netsh int ip reset and press Enter. Let it run.
3. Then, run netsh winsock reset and press Enter.
4. After that, run ipconfig /flushdns to clear old DNS entries.
5. Restart your PC and reconnect to the network.

These commands repair corrupted networking components that can cause address issues, so restart your PC.
Fix 4: Remove static IP duplicates or set DHCP
If your PC uses a static IP, switch it to automatic DHCP.
Open Settings, go to Network & Internet, select your adapter, and set IP assignment to Automatic (DHCP). Alternatively, assign a static IP outside the router’s DHCP range to avoid collisions.
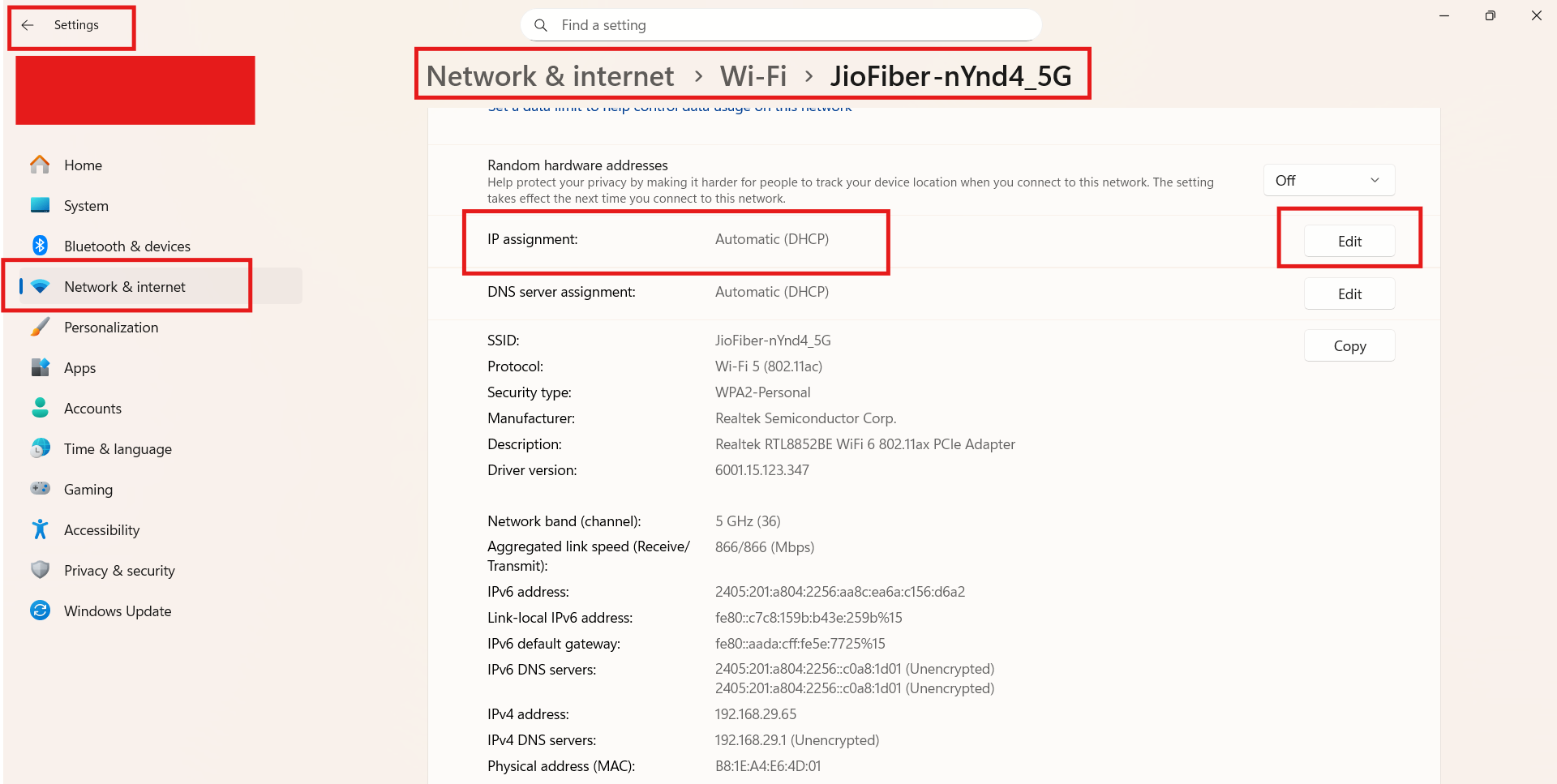
Fix 5: Update or reinstall network drivers
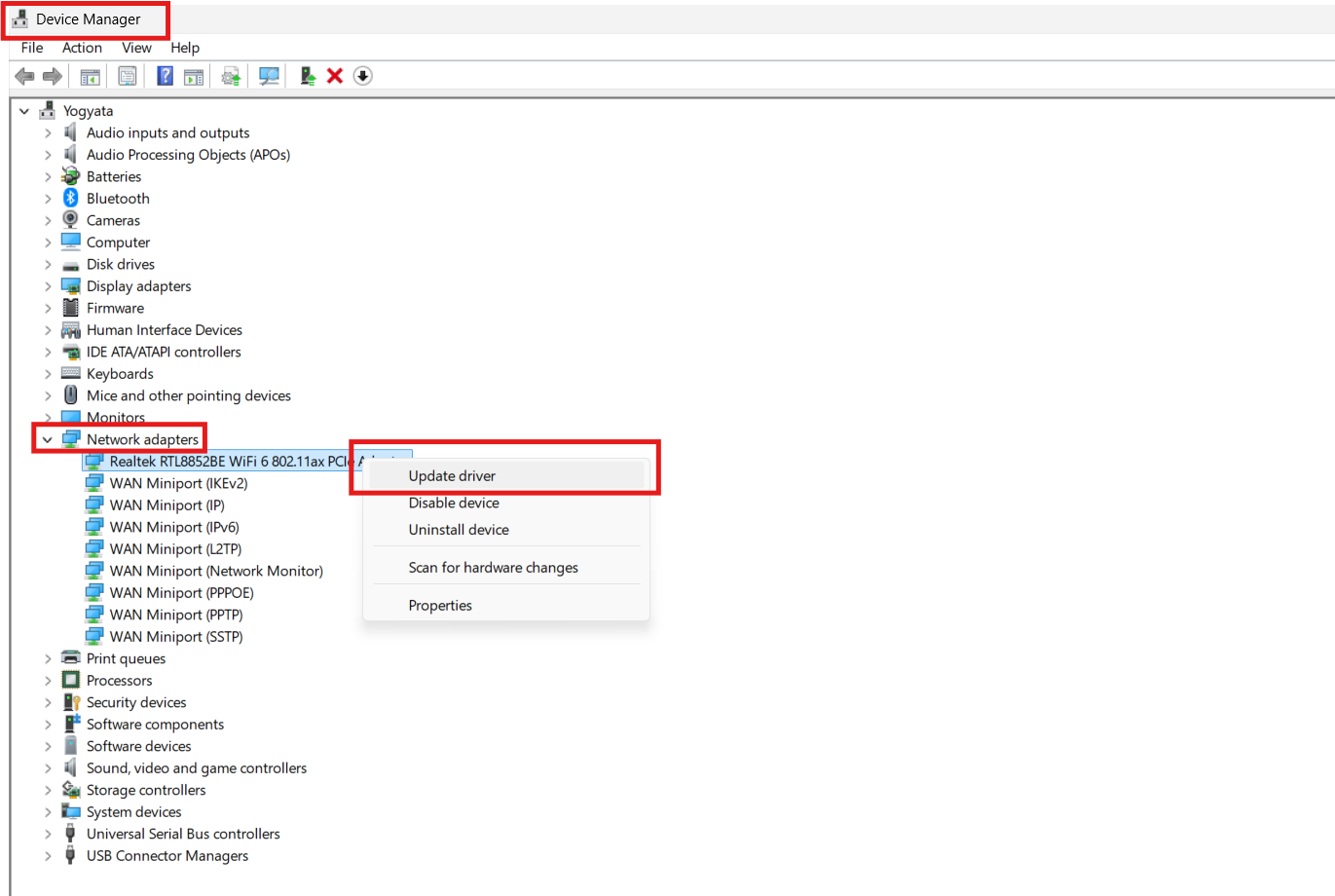
Outdated or damaged network drivers may cause Windows to assign incorrect or conflicting IP settings. Updating or reinstalling your driver ensures your network adapter communicates correctly with the router.
1. Open Device Manager.
2. Expand Network adapters and right-click your network device.
3. Choose Update driver and let Windows search for updates.
4. If the conflict continues, choose Uninstall device, restart your PC, and let Windows reinstall the driver automatically.
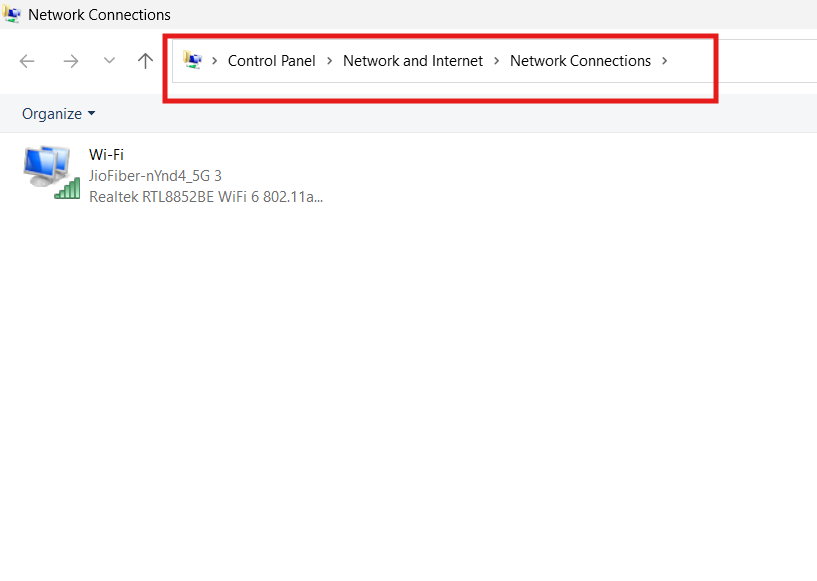
Fix 6: Disable conflicting virtual adapters or VPNs
Virtual adapters from VPNs, virtual machines, or software like VirtualBox can cause duplicate addresses.
Disable unused virtual adapters in Network Connections and test. Also, temporarily disable VPN clients to rule them out.
Fix 7: Check router DHCP settings and IP reservations
Log in to your router’s admin page and verify the DHCP range does not overlap with static IPs. Use DHCP reservations to bind IPs to device MAC addresses, which prevents accidental duplication. If in doubt, change the DHCP pool and reboot the network.
Quick tips
1. Identify the conflicting device by disconnecting devices one by one.
2. Use arp -a in Command Prompt to inspect current IP/MAC mappings.
3. If conflicts persist, contact your network administrator or ISP.


![Stop sharing a folder in Windows 11 [Guide] Stop sharing a folder in Windows 11 [Guide]](https://www.kapilarya.com/assets/Network.png)









Leave a Reply